Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * ▲ | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
07 Dec 2020
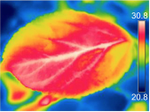
A new mechanism for tree mortality due to drought and heatwavesHervé Cochard https://doi.org/10.1101/531632A very useful simulation of the impact of drought and enhanced temperatures on embolism in trees and on tree diebackRecommended by Erwin Dreyer based on reviews by Sabine Rosner and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Sabine Rosner and 1 anonymous reviewer
Water availability has been known to strongly modulate forest productivity and tree growth on an interannual basis (as revealed by numerous dendrochronological studies) and across biomes (Ellison et al, 2017). Recurrent episodes of severe drought lead to decreased soil water content and as a consequence to visible losses in annual growth increment, and in some cases even to tree death and forest decline. The occurrence of such drought events and of larger scale tree dieback, seem to be increasing over the last decades, albeit such processes are not new. The causes for drought-induced tree death are still disputed; in many cases, tree death occurs after the release of drought, and is caused by severe attacks by pests and pathogens. In other cases, tree death is caused by recurrent drought events over several years, leading to a depletion of stored carbohydrates, growth decline and ultimately death. References Allen, C. D., Breshears, D. D., and McDowell, N. G. (2015). On underestimation of global vulnerability to tree mortality and forest die‐off from hotter drought in the Anthropocene. Ecosphere, 6(8), 1-55. doi: https://doi.org/10.1890/ES15-00203.1 | A new mechanism for tree mortality due to drought and heatwaves | Hervé Cochard | <p>Plants tend to die earlier in hot and drought conditions, but the underlying mechanisms are not yet understood. I propose here a new mechanism by which excessive residual water losses caused by high cuticular permeabilities and a high leaf-to-a... |  | Tree biology and physiology | Erwin Dreyer | 2020-03-03 09:33:12 | View | |
15 Apr 2024
Demographic and genetic impacts of powdery mildew in a young oak cohortBenoit Barrès, Cyril Dutech, Gilles Saint-Jean, Catherine Bodénès, Christian Burban, Virgil Fievet, Camille Lepoittevin, Pauline Garnier-Géré, Marie-Laure Desprez-Loustau https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.22.546164An interesting analysis of the interactions between English oaks (Quercus robur L.) and powdery mildew (Erisyphe sp.) at tree population level.Recommended by Erwin Dreyer based on reviews by Louis Bernier and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Louis Bernier and 1 anonymous reviewer
This preprint is recommended after a round of reviews by two external reviewers and the recommender and a careful revision of the initial text. The revision addressed all the the concerns raised by the reviewers and myself acting as recommender. I commend the authors for the care taken in the revision process and in addressing all concerns raised by the referees. The preprint is now in a status anabling a very positive recommendation, and I am convinced that PCI friendly journals will be keen to publish it given the quality of the contribution to Forest Pathology and Epidemiology as well as to and Forest Ecology. Indeed, the preprint adresses an important topic in forest ecology and forest management. Powdery mildew (due to a complex of fungi species of Erysiphe spp.) is a very frequent pathogen affecting oaks and mainly English oak (Quercus robur L.), a widespread species in Western European forests which bears great ecological and economic interests (see Marçais and Desprez-Loustau, 2014, for a review). Young regenerations are mostly affected by the disease, which infects young, unfoldling leaves and leads to severe reductions in photosynthesis (Hajji et al, 2009) and in some cases to tree dieback in young regenerations, and sometimes in older trees in the case of repeated infestations over several years, or combinations with defoliaitions by processionnary moths (Thaumetopoea processionea L.). Powdery mildew was introduced to Europe at the beginning of the 20th century and caused initially very severe damage in oak stands; currently, damage is much less prevalent, probably due to a co-evolution of the oak host and the pathogen (Desprez-Loustau and Marçais, 2019). The present investigation adds very interesting and important information to our current knowledge of this disease, and addresses in particular the genetic variability of susceptibility to the disease among oak families and the effect of the disease on the survival of seedlings in the long run. Five main research questions were addressed: i. How does powdery mildew affect juvenile survival; ii. Is the survival rate differing among oak families? iii. Does powdery mildew infection reduce the differences of fitness among oak families? iv. Does powdery mildew impact the genetic diversity of oak populations? v. Are there significant genetic associations between some genetic loci and seedling survival? These questions are important for unerstanding the evolution of a pathosystem like the powdery mildew/English oak system and for explaining the past dynamics of this pathosystem, which resulted in a dicrease in virulence of the disease since its introduction in Europe. The preprint reports results from a very original and solid experimental design based on the cultivation in the field of 15 oak progenies comprising 1733 indivduals over a quite long time span (9 years) and recurrent observations of growth, survival, infection intensity, ... A control group was protected against the pathogen by application of a fungicide. Moreover, a large number of individuals were genotyped, using single nucleatide polymorphism (SNP) allowing the detection of some candidate loci, and preparing future genome-wide association studies. The results are quite clear, and add very important elements to our understaning of this interesting and evolving pathosystem present in mots of the western European oak forests. This preprint is of particular interest since such approaches, which are becoming common in cultivated crops, have only seldom been applied to natural pathosystems despite their importance for the dynamics of forest ecosystems under the increasing impact of climate change. In brief, this is an important preprint that brings a large set of new data and addresses the urgent question of epidemiology of diseases in forest ecosystems. References Barrès B, Dutech C, Saint-Jean G, Bodénès C, Burban C, Fiévet V, Lepoittevin C, Garnier-Géré P, Desprez-Loustau M-L (2024) Demographic and genetic impacts of powdery mildew in a young oak cohort. bioRxiv, 2023.06.22.546164, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Forest and Wood Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.22.546164 Desprez-Loustau ML, Hamelin FM, Marçais B (2019) The ecological and evolutiionary trajectory of oak powdery mildew in Europe. In: Wilson K, Fenton A, Tompkins D, Wildlife Disease Ecology: Linking Theory to Data and Application. Ecological Reviews. Cambridge University Press, 978-1-107-13656-4. | Demographic and genetic impacts of powdery mildew in a young oak cohort | Benoit Barrès, Cyril Dutech, Gilles Saint-Jean, Catherine Bodénès, Christian Burban, Virgil Fievet, Camille Lepoittevin, Pauline Garnier-Géré, Marie-Laure Desprez-Loustau | <p style="text-align: justify;">The demographic and genetic impacts of powdery mildew on the early stages of an oak population were studied in an <em>ad hoc</em> field design with two disease exposures. This enabled a detailed phenotypic monitorin... | Interactions between trees and microorganisms, Population dynamics and genetics of forest trees | Erwin Dreyer | 2023-06-30 00:23:58 | View | ||
03 Aug 2022
Fire and forest loss in the Dominican Republic during the 21st CenturyJose Ramon Martinez Batlle https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.15.448604Spatio-temporal fire and forest loss patterns in the Dominican RepublicRecommended by Pauline Garnier-Géré based on reviews by Kevin Cianfaglione and 2 anonymous reviewersFires in the Anthropocene, whether natural or human-induced, are among the main factors of deforestation, threatening forest resilience and biodiversity (Kelly et al. 2020). Fire events have also increased in occurrence and severity worldwide in the past decade (e.g. Whitman et al. 2022, Ribeiro et al. 2020). In this context, we need to better understand the links between fire occurrence and their impact on forest loss, especially in countries where such knowledge is lacking. The work by Martinez-Batlle addresses this need as it thoroughly describes forest loss and fire patterns across the forests of the Dominican Republic (DR), and systematically tests their spatial and temporal correlations across the DR regions since 2001. To this end, the author combines two independent databases from NASA: the Global Forest Change 2000-2018 data service, and remotely sensed data on fire/hotspot occurrence. The author then provides a state-of-the-art analysis pipeline that first shows significant spatial autocorrelations in both forest loss and fire density over the whole period, and each year across the period. Detailed maps of zonal statistics across hexagonal grids also illustrate clusters of either high or low forest loss and fire points, and distinguish small or large clearings. Second, these spatial dependencies are accounted for in spatial autoregressive models, and congruent patterns of forest loss and fire density are shown across the 2001-2018 period in the DR. This is consistent with the initial working hypothesis of a link between deforestation and slash and burn agriculture. Third, detailed time-series analyses and modelling show common cyclical patterns for forest loss areas in large clearings, number of small clearings, and fire density in the first 14 years, with no increasing trends. In contrast, fire density does not predict extensive forest loss in the eastern half of the country for most years. Finally, yearly maps clearly depict uncontrolled wildfires that impacted larger areas in recent years in both the central and southern mountain ranges of the DR. This work, therefore, provides a solid, detailed, and rigorous account of the current status of forest loss across the DR, and of its causes, either from recurrent fires due to shifting agriculture or from farming linked to tourism expansion. These results could be very useful for designing strategies adapted to each particular zone of the DR, for preventing human-induced fires or managing wildfires, and for planning post-fire reforestation. This is true, especially for core protected areas where an increasing trend of forest loss is identified in the last 8 years (up to 25% in some mountainous and inaccessible areas of the DR). In those areas, the author suggests implementing a natural regeneration program. Indeed, recent scientists’ warnings stress that fires should be accounted for when planning reforestation for climate change mitigation (Leverkus et al. 2022), with evidence in different ecosystems, that natural regeneration with local seed banks would benefit their post-fire recovery. As proposed by the author, this new knowledge for the DR should also help develop policies for managing forest fires and biodiversity, which are lacking in areas close to tourism facilities. More generally, this study offers methods and graphical representations that are likely to inspire future work with similar databases in other countries where data are scarce, on either spatial trends or temporal evolution of forest cover, or fire activities, or both. Kelly LT, Giljohann KM, Duane A, Aquilué N, et al. (2020). Fire and biodiversity in the Anthropocene. Science, 370(6519), eabb0355. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb0355 Leverkus AB, Thorn S, Lindenmayer DB, Pausas JG (2022) Tree planting goals must account for wildfires. Science 376(6593): 588-589. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abp8259 Martinez Batlle JR (2022) Fire and forest loss in the Dominican Republic during the 21st Century. bioRxiv, 2021.06.15.448604, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Forest and Wood Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.15.448604 Ribeiro LM, Viegas DX, Almeida M, McGee TX, et al. (2020) 2 - Extreme wildfires and disasters around the world: lessons to be learned. In F. Tedim, V. Leone, T.K. McGee (Eds.), Extreme Wildfire Events and Disasters, Elsevier Inc. 31-pp. 51. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815721-3.00002-3 Whitman et al. (2022) Climate-induced fire regime amplification in Alberta, Canada. Environ. Res. Lett. 17(5): 055003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac60d6 | Fire and forest loss in the Dominican Republic during the 21st Century | Jose Ramon Martinez Batlle | <p>Forest loss is an environmental issue that threatens ecosystems in the Dominican Republic (the DR). Although shifting agriculture by slash-and-burn methods is thought to be the main driver of forest loss in the DR, empirical evidence of this re... | Forest history, Forest policies , Silviculture and forest management | Pauline Garnier-Géré | 2021-11-13 17:04:31 | View | ||
22 Feb 2021

High-quality SNPs from genic regions highlight introgression patterns among European white oaks (Quercus petraea and Q. robur)Tiange Lang, Pierre Abadie, Valérie Léger, Thibaut Decourcelle, Jean-Marc Frigerio, Christian Burban, Catherine Bodénès, Erwan Guichoux, Grégoire Le Provost, Cécile Robin, Naoki Tani, Patrick Léger, Camille Lepoittevin, Veronica A. El Mujtar, François Hubert, Josquin Tibbits, Jorge Paiva, Alain Franc, Frédéric Raspail, Stéphanie Mariette, Marie-Pierre Reviron, Christophe Plomion, Antoine Kremer, Marie-Laure Desprez-Loustau, Pauline Garnier-Géré https://doi.org/10.1101/388447A new resource for a better understanding of the complex genetic dynamics within the oak syngameonRecommended by Erwin Dreyer based on reviews by Oliver Brendel, Ricardo Alia, Komlan Avia and Hilke Schröder based on reviews by Oliver Brendel, Ricardo Alia, Komlan Avia and Hilke Schröder
When we launched the multidisciplinary PCI Forest and Wood Sciences, we were well aware that this PCI devoted to a broad object (forests represent 1/3 of the emerged land area) and gathering multiple disciplines (from biology to social sciences), would be confronted with some challenges with respect to the range of pre-prints we would have to consider. Among the first ones submitted to the new PCI was this very interesting one (Lang et al, 2021) in the area of tree genomics and tree population genetics with a strong background in bioinformatics. This could well have been submitted to the PCI in Genomics, or the PCI in Evolutionary Biology, but finally fits very well in PCI Forest and Wood Sciences due to its finality: provide reliable genomic resources to tackle questions that are central to our understanding of the dynamics of forest ecosystems and the adaptation of trees to local conditions. References Cannon CH, Petit RJ (2020) The oak syngameon: more than the sum of its parts. New Phytologist, 226, 978–983. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16091 | High-quality SNPs from genic regions highlight introgression patterns among European white oaks (Quercus petraea and Q. robur) | Tiange Lang, Pierre Abadie, Valérie Léger, Thibaut Decourcelle, Jean-Marc Frigerio, Christian Burban, Catherine Bodénès, Erwan Guichoux, Grégoire Le Provost, Cécile Robin, Naoki Tani, Patrick Léger, Camille Lepoittevin, Veronica A. El Mujtar, Fran... | <p>In the post-genomics era, non-model species like most Fagaceae still lack operational diversity resources for population genomics studies. Sequence data were produced from over 800 gene fragments covering ~530 kb across the genic partition of E... |  | Population dynamics and genetics of forest trees | Erwin Dreyer | 2020-03-03 08:00:45 | View | |
14 Oct 2020

Interaction of drought and frost in tree ecophysiology: rethinking the timing of risksGuillaume Charrier, Nicolas Martin-Stpaul, Claire Damesin, Nicolas Delpierre, Heikki Hänninen, José Torres-Ruiz, Hendrik Davi https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02475505v4Giving a temporal context to drought and frost vulnerability of treesRecommended by Rosana López based on reviews by Jordi Martínez Vilalta and Sean GleasonRange limits of forest species are frequently imposed by spatial gradients in climatic variables. Tolerance to maximum and minimum temperatures, including short-term extremes, and tolerance to desiccation are crucial limiting factors for plant survival and often appear interrelated (Box 1995; Choat et al. 2018). Increasing temperatures, more frequent and extreme droughts and late frost events associated with global climate change will affect the dynamics of forest ecosystems and have the potential to dramatically increase plant mortality and accelerate species range shifts if plants are not able to adapt in situ to the novel climate regimes (Parmesan 2006; Choat et al., 2012). This is particularly important at species range edges, where climatic conditions may not be sufficient to impose mortality on individuals directly, but trees experience greater physiological stress, which influences such factors as dispersal, habitat selection, and subsequent reproductive fitness (Parmesan 2006). In such marginal situations, where gene flow may be also restricted (López de Heredia et al. 2010), the effectiveness of adjustment through natural selection is limited resulting in increased vulnerability to extreme climatic events and to a higher risk of mortality of trees. References Anderegg WR, Schwalm C, Biondi F, Camarero JJ, Koch G, Litvak M, Ogle K, Shaw JD, Shevliakova E, Williams A (2015) Pervasive drought legacies in forest ecosystems and their implications for carbon cycle models. Science 349: 528–532. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aab1833 | Interaction of drought and frost in tree ecophysiology: rethinking the timing of risks | Guillaume Charrier, Nicolas Martin-Stpaul, Claire Damesin, Nicolas Delpierre, Heikki Hänninen, José Torres-Ruiz, Hendrik Davi | In temperate, boreal and alpine areas, the edges of plant distribution are strongly affected by abiotic constraints. For example, heat waves and drought are major constraints at low latitude and elevation while cold and frost are key factors at hi... |  | Tree biology and physiology | Rosana López | 2020-04-28 21:07:27 | View | |
08 Jul 2022
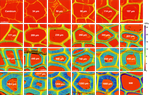
Mechanical characterisation of the developing cell wall layers of tension wood fibres by Atomic Force MicroscopyOlivier Arnould, Marie Capron, Michel Ramonda, Françoise Laurans, Tancrède Alméras, Gilles Pilate, Bruno Clair https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.23.461481“Touching the Void”Recommended by Barry Gardiner based on reviews by Meriem Fournier and Félix HartmannUnderstanding the processes allowing trees to orientate their stems and branches requires an understanding of the mechanical properties of individual cells. As the cells are formed, maturation stresses are created that can lead to the reorientation of the tree. But measuring the properties within the different wood cells produced in normal wood, tension wood or compression wood requires measurements at very fine spatial resolution and the wood cells must remain in-situ so that the cell mechanical characteristics are preserved. In the article of Arnould et al (2022), measurements of the mechanical characteristics of poplar tension wood were measured in comparison to normal wood at different distances from the cambium and therefore different levels of maturation. The work required incredible care to embed the wood in resin, to cut the wood with extremely sharp microtone blades in order to minimize artefacts in the measurements, and then ultra-careful atomic force microscope (AFM) measurements across cell walls from the edge of the lumen to the middle lamella at extremely high spatial resolution. The result is a detailed picture of the kinetic development and maturation of tension wood cells in a tree. The measurements showed that the G-layer reaches close to its final stiffness long before its final thickness, and this is different from the maturation kinetics of other cell wall layers where thickening and stiffening are generally synchronous. Finally, although the G-layer in poplar tension wood fibres and in flax phloem fibres are in many ways very similar there are clear differences in the kinetics of their development and maturation. The detailed information presented in this paper can therefore help to clarify the different hypothetical mechanisms proposed to explain excess stress generation in the tension wood of trees and help move us towards a full understanding of how the “muscles” of trees work. References Arnould O, Capron M, Ramonda M, Laurans F, Alméras T, Pilate G, Clair B (2022) Mechanical characterisation of the developing cell wall layers of tension wood fibres by Atomic Force Microscopy. bioRxiv, 2021.09.23.461481, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Forest and Wood Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.23.461481 | Mechanical characterisation of the developing cell wall layers of tension wood fibres by Atomic Force Microscopy | Olivier Arnould, Marie Capron, Michel Ramonda, Françoise Laurans, Tancrède Alméras, Gilles Pilate, Bruno Clair | <p style="text-align: justify;">Trees generate mechanical stresses at periphery of stem and branches to improve their strength and to control the orientation of their axes. This key factor in the biomechanical design of trees, named “maturation st... |  | Biology of wood in living trees | Barry Gardiner | 2022-01-11 17:49:47 | View | |
03 May 2023

Modelling the growth stress in tree branches: eccentric growth vs. reaction woodArnoul VAN ROOIJ, Eric BADEL, Jean Francois BARCZI, Yves CARAGLIO, Tancrède ALMERAS, Joseph GRIL https://hal.science/hal-03748026An important contribution to the description of growth stresses in branches of adult trees based on a new model and an optimisation process with digitised branches.Recommended by Erwin Dreyer based on reviews by Jana Dlouha and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jana Dlouha and 1 anonymous reviewer
This interesting article (van Rooij et al, 2023) proposes an innovative modelling approach to the question of the biomechanics of a growing branch. The main aim is to model the “growth stress” (Fournier et al, 2013) it is exposed to while developing its radial structure in response to increasing weight. The proposed model is very interesting and novel with respect to the existing literature on this important topic in tree biology. The model bases on two major components of the structure of a growing branch: the eccentricity (the branch is usually thicker vertically than horizontally, which may provide the strength to resist the weight) and the production of reaction wood (Barnett et al, 2014) on one side of the branch which produces asymmetric forces against gravity. The reaction wood is either tension wood (in hardwood trees, e.g., angiosperms) or compression wood (in softwood trees, e.g., gymnosperms). The model is clearly described and based on a number of explicit and already described concepts with some simplifications (no local irregularities like nodes or holes, only vertical bending taken into account, branch growing straight at a constant angle, …) whose potential effects are nicely discussed and on a reliable and detailed set of analytical equations. The model addresses the dynamic changes resulting from branch growth, i.e., mainly radial growth which results in an accumulation of wood and in increasing mass and “growth stress”. The model is tested during a virtual experiment using a small set of data from a large pine tree (taken as an example of a softwood conifer tree) and a cherry tree (taken as an example of a hardwood tree). The optimisation test uses the mean allometric values from 30 branches of each individual tree as an entry to the model. This test of the optimality of the model is a very useful prerequisite for the adoption of the model. One might however argue that some replicate examples from other tree species would have been welcome to better represent the potential inter-specific variability in the two groups (softwoods vs. hardwoods). Indeed, there is a lack of suitable data available to properly test the underlying hypotheses under different conditions (growth angles, wood densities, growth rate, branch aging, ….). However, the presented computations allow testing the plausibility of the model and of its main conclusions, with respect to some “growth stress” values reported in the literature. The results confirm that the contribution of reaction wood is dominant, even if the eccentricity of the branches bears a significant contribution in the two tested cases. The present preprint has the potential to act as the foundation for some additional research that might challenge its main conclusions and provide (hopefully) more support to the main conclusion that eccentricity plays a minor but still significant role in ensuring the stability of the growing branches and that the main stabilising effects are produced by reaction wood. This version of the preprint is now suitable for a recommendation. However, it still suffers a few minor typos and language issues that the authors might correct during further steps in the publication process (a final version as a preprint, or submission to a journal chosen by the authors). Among those typos, the fact that Prunus avium is a cherry tree and not a birch. Similarly, several references need be corrected and completed, and more care should be in general given to the scientific species names…. In conclusion, this modelling exercise and the optimisation procedure used here underline once more the importance of reaction wood as a stabiliser of the three-dimensional architecture of trees not only in the trunk (where it has been studied in detail), but also in the lateral and sometimes quite heavy branches. Anyway, I believe this preprint (and the version potentially published in a journal) will become an important reference for future research about the biomechanics of branches and of tree crowns in general, and that it will trigger further research in this direction. REFERENCES Arnoul van Rooij, Eric Badel, Jean-François Barczi, Yves Caraglio, Tancrede Almeras, and Joseph Gril. (2023) Modelling the growth stress in tree branches: eccentric growth vs. reaction wood. HAL, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Forest and Wood Science. https://hal.science/hal-03748026v4 Mériem Fournier, Jana Dlouha, Gaëlle Jaouen, Tancrède Almeras (2013). Integrative biomechanics for tree ecology: beyond wood density and strength. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60 (15), pp.4397- J.R. Barnett, Joseph Gril, Pekka Saranpää (2014) Introduction, In: The Biology of Reaction Wood, Springer Series in Wood Science, Springer (pub), Gardiner B., Barnett J., Saranpää P., Gril J (eds), p. 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-10814-3_1 | Modelling the growth stress in tree branches: eccentric growth vs. reaction wood | Arnoul VAN ROOIJ, Eric BADEL, Jean Francois BARCZI, Yves CARAGLIO, Tancrède ALMERAS, Joseph GRIL | <p style="text-align: justify;">This work aims to model the mechanical processes used by tree branches to control their posture despite their increasing weight loading. The two known options for a branch to maintain its orientation are the asymmet... |  | Biology of wood in living trees | Erwin Dreyer | 2022-08-25 14:12:06 | View | |
08 Aug 2023

Pollen contamination and mating structure in maritime pine (Pinus pinaster Ait.) clonal seed orchards revealed by SNP markersLaurent Bouffier, Sandrine Debille, Pierre Alazard, Annie Raffin, Patrick Pastuszka, Jean-François Trontin https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.27.509769New insights in seed orchards pollen contamination, study case in an advanced breeding programRecommended by Ricardo Alia based on reviews by Eduardo Notivol and 1 anonymous reviewerThis preprint (Bouffier et al, 2023) analyses different biological (tree genotype, age, flowering phenology) and environmental factors (vicinity with external pollen sources, orchard structure, soil type, climatic conditions) with influence on the of seed lots in seed orchards of an important forest tree species (Pinus pinaster Ait.). The analysis is based on an optimized set of 60 SNP markers that constitute a new tool for characterizing improved material in the breeding program of the species. One of the main questions when managing seed orchard is to obtain a precise estimation of pollen contamination, as it causes major losses to genetic improvement from selection and breeding (Di Giovanni and Kevan, 19911) but also will determine the adaptive potential of the species (Kremer et al. 2012). The results indicate that contamination rates were highly variable between seed lots (from 20 to 96%), with a mean value of 50%). The main factors determining these rates include the distance between the seed orchard and external pollen sources, rain during the pollination period, seed orchard age, soil conditions and seed parent identity. A second point of interest in this paper is the determination of the overall self-fertilization rate. This factor also determines the quality of the seed-lots and was estimated as 5.4%, with high variability between genotypes (from 0% to 26%). The overall value is of the same order of magnitude than in other species. These results are used to define some recommendations for managing seed orchards in the French breeding program, but that can be generalized to other species (eg. Mullin and Lee, 2013). As an example, they recommend that sampling 100 seeds annually should be sufficient to estimate pollen contamination (with a standard error of 5%). Also, they suggest that one of the main measures to reduce pollen contamination is carefully selecting the location of the orchard, in terms of its distance from external pollen sources and soil conditions, and not collecting seeds from young trees (below 8 years old). The present preprint revisits an important topic of research with interest for the biology of tree species, but also with great implications in applied breeding activities. The main conclusions are essential to understand the importance of different factors in managing seed orchards and in the future performance of the reproductive material. In conclusion, this paper stresses the need for more studies, taking advantage of new genomic tools, to advance the knowledge of factors influencing the success of breeding programs. REFERENCES Bouffier L, Debille S, Alazard P, Raffin A, Pastuszka P, Trontin JF (2023). Pollen contamination and mating structure in maritime pine (Pinus pinaster Ait.) clonal seed orchards revealed by SNP markers. bioRxiv, 2022.09.27.509769, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Forest and Wood Science. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.27.509769 Di-Giovanni F, Kevan PG (1991) Factors affecting pollen dynamics and its importance to pollen contamination: a review. Can J For Res 21(8):1155-1170. Mullin TJ, Lee SJ (2013) Best practice for tree breeding in Europe. Skogforsk, Uppsala, Sweden. ISBN: 530 978-91-977649-6-4. https://www.skogforsk.se/contentassets/42acda01f83843bf925f690bd0a6ed37/best-practice-hela-low.pdf | Pollen contamination and mating structure in maritime pine (*Pinus pinaster* Ait.) clonal seed orchards revealed by SNP markers | Laurent Bouffier, Sandrine Debille, Pierre Alazard, Annie Raffin, Patrick Pastuszka, Jean-François Trontin | <p style="text-align: justify;">Maritime pine (<em>Pinus pinaster</em> Ait.) is a major forest tree species in south-western Europe. In France, an advanced breeding program for this conifer species has been underway since the early 1960s. Open-pol... |  | Population dynamics and genetics of forest trees, Silviculture and forest management | Ricardo Alia | 2022-09-29 11:39:50 | View | |
12 Jul 2021
Tree growth forces and wood propertiesBernard Thibaut, Joseph Gril https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02984734Into the wood: the biomechanical history of trees revealed by their inner structureRecommended by Hervé Cochard based on reviews by Barry Gardiner and 1 anonymous reviewerTrees are constantly subjected to mechanical stresses (gravity, wind, storms) but they have a remarkable ability to remain upright despite their great size. Straightness is also major characteristic that greatly determines the quality and market value of a log. For some species, maritime pine in particular, this is even a default that geneticists are trying to correct through dedicated breeding programs (Bartholomé et al. 2016). If trees are able to maintain a straight trunk, or to return to straightness after a growth accident, for example, it is thanks to an "engine" whose mechanisms are now better known (Moulia et al. 2021). This mechanism lies in the structure of the trunk itself and the ability of trees to produce cells and tissues that display different mechanical properties during their maturation. Some fibers will "pull" the trunk in one direction, known as tension wood, while others will « push » it in the opposite direction (compression wood). The posture control of a tree is therefore directly related to the growth process of the trees and the placement of this reaction wood at specific points in the trunk. The internal structure of the trunk will therefore retain the memory of these growth constraints throughout its life and, if we are able to read it, we can envisage reconstructing its history over the years. This source of information contained in tree rings is still largely unexplored. However, it can reveal insights into the evolution of the climate, or help foresters to select the most valuable trees. Sophisticated approaches exist to measure these growth forces in wood, but the major difficulty remains our ability to read the mechanical properties with simpler, more widely used methods. The article by Thibaut and Gril (2021) proposes such a methodology. The approach used here is similar to the one used for other wood functions, such as sap transport: linking the mechanical function of wood to its structural properties. The transport capacity of wood is for example well explained by the distribution of vessel sizes. However, other interesting properties, such as resistance to cavitation, are only very weakly explained by the same anatomical characteristics. The authors, after analyzing the wood properties of many species, both tropical and temperate, conclude that growth forces can be deduced from variables that are relatively simple to measure, such as wood density or moduli of elasticity. The article provides a series of generic and more specific equations and relationships that allow these growth forces to be estimated. I recommend this article to people who want to learn about the principles and concepts of tree biomechanics. I also recommend it to people who want to further explore the mechanical properties of trees and who will be able to characterize them thanks to the method proposed here by the authors. References Bartholomé J, Bink MC, Heerwaarden J van, Chancerel E, Boury C, Lesur I, Isik F, Bouffier L, Plomion C (2016) Linkage and Association Mapping for Two Major Traits Used in the Maritime Pine Breeding Program: Height Growth and Stem Straightness. PLOS ONE, 11, e0165323. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0165323 Thibaut B, Gril J (2021) Tree growth forces and wood properties. HAL, hal-02984734, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Forest and Wood Sciences. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02984734 Moulia B, Douady S, Hamant O (2021) Fluctuations shape plants through proprioception. Science, 372. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abc6868 | Tree growth forces and wood properties | Bernard Thibaut, Joseph Gril | <p style="text-align: justify;">Living wood in the tree performs a “muscular” action by generating forces at the sapwood periphery and residual strains in dead sapwood fibres. Dissymmetric force generation around the tree trunk is the “motor” syst... | Biology of wood in living trees , Wood properties and wood products | Hervé Cochard | 2020-11-06 10:41:38 | View | ||
15 Mar 2021

Variability in seeds’ physicochemical characteristics, germination and seedling growth within and between two French Populus nigra L. populationsMarlène Lefebvre, Marc Villar, Nathalie Boizot, Armelle Delile, Benjamin Dimouro, Anne-Marie Lomelech, Caroline Teyssier https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.05744Black poplar (Populus nigra L.) seed physiology: an important issue for the in situ conservation of this riparian speciesRecommended by Erwin Dreyer based on reviews by Tomasz A. Pawlowski, Eduardo Notivol and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Tomasz A. Pawlowski, Eduardo Notivol and 1 anonymous reviewer
Seed physiology, which was a little forgotten in forest ecology since several decades, needs be revitalized as a research area given the many open questions about population dynamics and demography in rapidly changing environments (and not only for endangered species). Indeed, seed physiology was long mobilized mainly to optimize seed conservation and germination for the production of plant material in a range of tree species used for afforestation/plantation. In the case of back poplar (which by the way is the male genitor of the multiple hybrid Populus x euramerica poplar cultivars), the focus is rather on the conservation ecology of this riparian species, and mainly on in situ conservation (Lefèvre et al, 1998). Indeed, the protection of populations of Populus nigra L requires an improved understanding of the ecology of this species with a focus on reproduction. Indeed, black poplar seeds need to be rapidly disseminated, to germinate as soon as the conditions are favourable (with rather small time windows) and establish seedlings with access to water in the rather harsh environment of mobile and sandy river banks submitted to alternating periods of flooding and of severe water deficits during low river flows in summer (Imbert and Lefèvre, 2003; Corenblit et al, 2014; Tinschert et al, 2020). This process is therefore central to the propagation/maintenance of these populations that are threatened by the destruction of river banks and by introgression by either genes from the widespread “Italica” cultivar of black poplar, of from other poplar species leading to a variety of natural hybrids (Smulders et al, 2008). Many questions remain open about seeds of black poplar (Michalak et al, 2015). One of the most intriguing one is to what extent seed properties and physiology differ within and among local populations from different river catchments. This question was addressed in this preprint by Lefebvre et al. (2021) that provides a very detailed and comparative analysis of two populations from central and southern France, each represented by 10 half sib families (i.e., seed collected separately from 10 adult individuals after open pollination). Investigated properties were mainly seed biomass, anatomy, germination rate, root growth, lipid and sugar contents, protein content (with identification of some major protein families). The within populations variability was indeed quite large, but nevertheless there were significant differences between the two populations in several traits, like seed weight, lipid content, and starch content. Storage proteins differed among families, but only slightly between the two populations. However, the main conclusion was that intrinsic qualities of the seeds were not critical for early stage establishment in the two populations, despite some significant differences in mean seed biomass, in lipid and in soluble sugars contents. The preprint nicely analyses these differences, brings a large set of new observations about the seed physiology of Populus nigra. The referees found the data produced during this research quite important and original. This is why, despite the fact that the number of tested groups of populations remains rather small and the link with seedling establishment remains rather weak, this study is an important contribution to conservation ecology. This research (and that of many other groups) needs be further developed with an emphasis on inter and intra population variation and on demogenetics of forest tree species. References Corenblit D., Steiger J., González, E et al. (2014), The biogeomorphological life cycle of poplars during the fluvial biogeomorphological succession: a special focus on Populus nigra L.. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms, 39: 546-563. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3515 Imbert E. and Lefèvre F. (2003) Dispersal and geneflow of Populus nigra (Salicaceae) along a dynamic river system. Journal of Ecology 91: 447-456. doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2745.2003.00772.x Lefebvre M., Villar M., Boizot N., Delile A., Dimouro B., Lomelech A.-M. and Teyssier, C. (2021) Variability in seeds’ physicochemical characteristics, germination and seedling growth within and between two French Populus nigra populations. arXiv, 2008.05744, ver 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Forest and Wood Sciences. https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.05744 Lefèvre F., Légionnet A., de Vries S. and Turok J. (1998) Strategies for the conservation of a pioneer tree species, Populus nigra L., in Europe. Genetics, Selection, Evolution 30, S181-196. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1297-9686-30-S1-S181 Michalak M., Plitta B.P., Tylkowski T. et al. (2015) Desiccation tolerance and cryopreservation of seeds of black poplar (Populus nigra L.), a disappearing tree species in Europe. European Journal of Forest Research 134, 53–60. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-014-0832-4 Smulder M.J.M., Beringen R., Volosyanchuk R. et al. (2008) Natural hybridisation between Populus nigra L. and P. x canadensis Moench. Hybrid offspring competes for niches along the Rhine river in the Netherlands. Tree Genetics & Genomes 4, 663–675. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-008-0141-5 Tinschert E., Egger G., Wendelgass J. et al. (2020) Alternate reproductive strategies of Populus nigra influence diversity, structure and successional processes within riparian woodlands along the Allier River, France. Journal of Hydro-environment research 30, 100-108. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2020.03.004 | Variability in seeds’ physicochemical characteristics, germination and seedling growth within and between two French Populus nigra L. populations | Marlène Lefebvre, Marc Villar, Nathalie Boizot, Armelle Delile, Benjamin Dimouro, Anne-Marie Lomelech, Caroline Teyssier | <p>To improve understanding of the physiology, ecology and regeneration requirements of black poplar (Populus nigra), a severely endangered tree species in Europe, we analysed the biochemical composition of seeds from 20 families derived from open... |  | Tree biology and physiology | Erwin Dreyer | 2020-08-14 09:59:17 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Erwin Dreyer
Francis Martin
Jean-Michel Leban
Hervé Cochard
Jürgen Bauhus
Laurent Augusto
Eric Badel
Serge Garcia










